MineRL: Learn Minecraft from Human Priors

What it is
MineRL is a competition for the upcoming NeurIPS 2019 conference. The competition uses the Minecraft environment, and the goal of the participants is to train the agent to obtain diamonds. This is a very difficult task, so the organizers also provide the MineRL dataset, which is a large-scale dataset of human demonstrations.
The competition started a few days ago and will end on October 25th. According to the organizers, Preferred Networks will be releasing a set of baselines for the competition soon.
Why it matters
Reinforcement learning competitions are amazing opportunities for new RL researchers to gain first-hand experience. MineRL offers a unique opportunity by providing human demonstration data. It is difficult for individual researchers to collect large amount of demonstrations to test their ideas. The competition alleviates this problem and allows researchers to implement their own algorithms without worrying about collecting data.
Read more
- NeurIPS 2019: MineRL Competition (AICrowd)
- MineRL Project (Project Website)
- MineRL Minecraft Server (Project Website)
- MineRL Dataset Description (Project Website)
- MineRL Documentation (Read the Docs)
- The MineRL Competition on Sample Efficient Reinforcement Learning using Human Priors (ArXiv Preprint)
External Resources
- 2017 The Malmo Collaborative AI Challenge
- 2018 Learning to Play: the Mutli-agent Reinforcement Learning in MALMÖ (MARLÖ) Competition
Off-Policy Evaluation via Off-Policy Classification
What it is & Why it matters
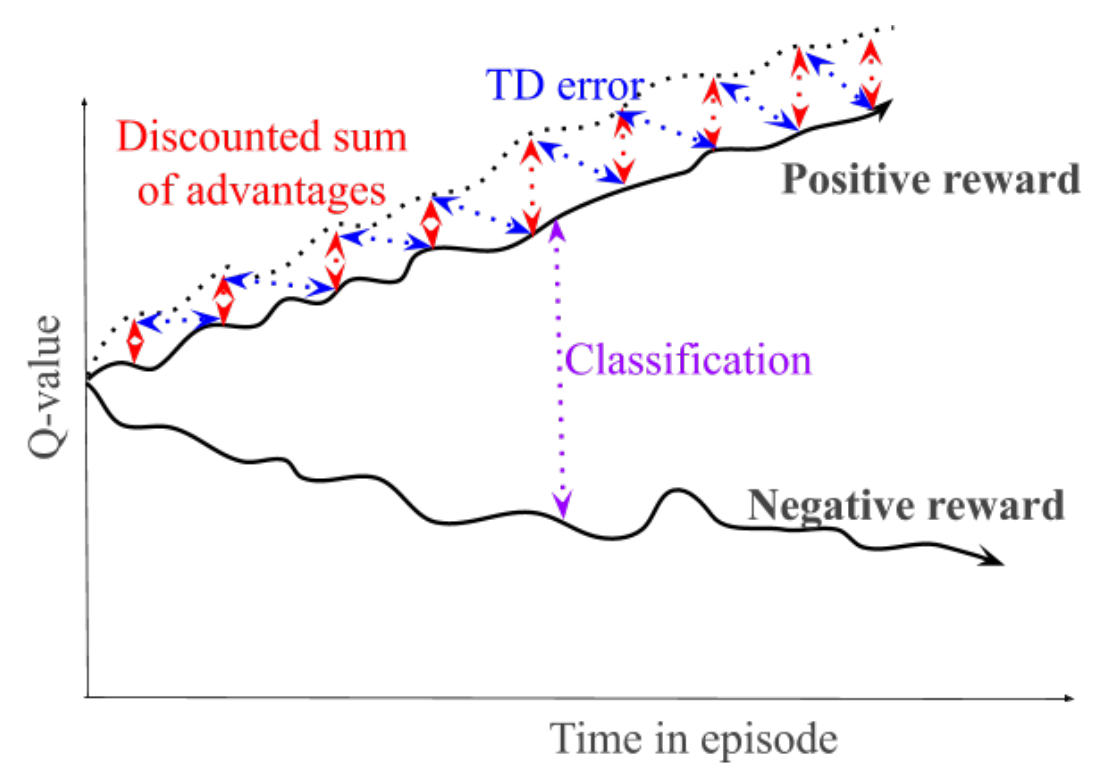
Traditionally, a trained agent is evaluated by interacting with the target environment. Although this is feasible when the target environment is a simulated environment, it may be problematic in real-life applications like robotics. In these cases, off-policy evaluation (OPE) methods should be used. Different from existing OPE methods that require a good model of the environment or use importance sampling, this paper frames OPE as a “positive-unlabeled” classification problem. A state-action pair is labeled “effective” if an optimal policy can achieve success in that situation, and “catastrophic” otherwise. The intuition lies in that a well-learnt Q-function should return high value for effective state-action pair and low value for catastrophic state-action pair.
Read more
- Off-Policy Evaluation via Off-Policy Classification (ArXiv Preprint)
- Code for the Binary Tree Environment (GitHub Gist)
Towards Interpretable Reinforcement Learning Using Attention Augmented Agents
What it is & Why it matters
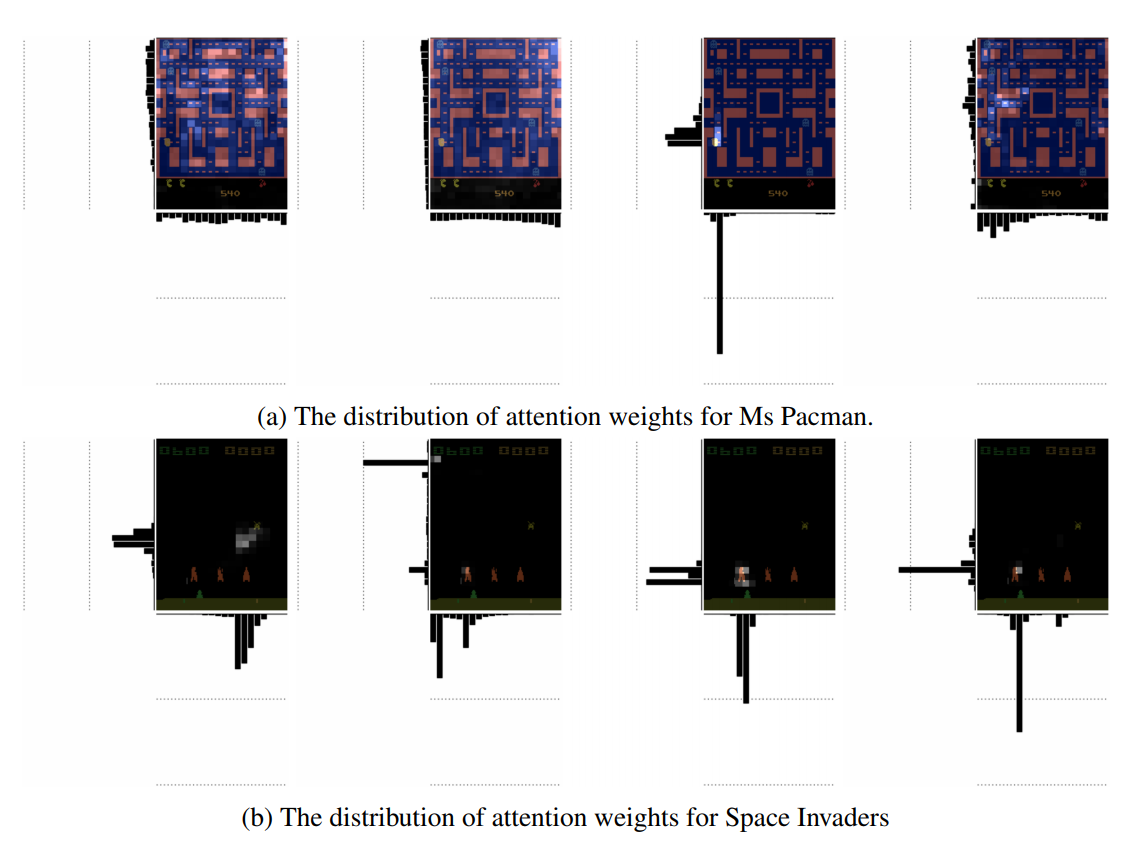
The authors propose a LSTM architecture with a soft, top-down, spatial attention mechanism. The paper is not the first to propose using attention in RL agents, but the numerous experiments show how attention can be used to qualitatively evaluate and interpret agents’ abilities. The project website below shows how attention can be used to understand how the agent reacts to novel states, how the agent plans, and what the agent’s strategy is.
Read more
- Towards Interpretable Reinforcement Learning Using Attention Augmented Agents (ArXiv Preprint)
- Towards Interpretable Reinforcement Learning Using Attention Augmented Agents (Project Website)
Some more exciting news in RL:
- Researchers at Google Research open-sourced Google Research Football, an RL environment for football.
- Researchers at Electronic Arts and Institute of Computational Modelling trained Non-Player Characters (NPCs) in video games through imitation learning with a human in the loop.
- Researchers at OpenAI performed an empirical study to show the relationship between hyperparameters and generalization.
- Researchers at Nanjing University proposed Clustered RL that divides collected states into clusters and defines a clustering-based bonus reward to incentivise exploration.
- Researchers at MIT, Harvard, Diffeo, and CBMM developed DeepRole, a multi-agent RL agent that learns who to cooperate with and outperforms humans in the game The Resistance: Avalon.
- Researchers at DeepMind and University of Toronto proposed OPRE (OPtions as REsponses), a multi-agent hierarchical agent.
- Researchers at University of Oxford propose Independent Centrally-assisted Q-Learning (ICQL) that allow using intrinsic rewards for multi-agent RL.
- Researchers at Microsoft Research Montreal and Imperial College London hypothesized that the poor performance of low discount factors are not due to small action-gaps but due to “the size-difference of the action gaps across the state-space.”